Science
Lindis BiotechScience | What we do
We combine leading scientific expertise in tumor immunotherapy and Triomab® antibody technology.
Mode-of-Action
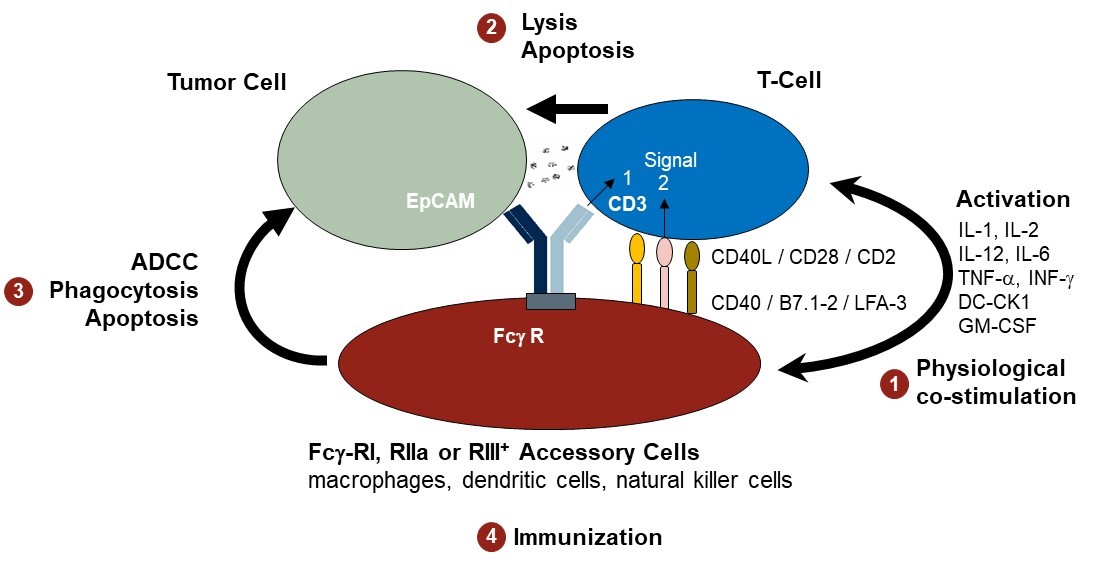
Triomab® antibodies induce a highly potent immune response against the tumor
T-cells are redirected to and activated at the tumor cells in an MHC-independent manner by Triomab® antibody-mediated crosslink of tumor-associated antigens (TAA) with CD3 (signal 1).
Simultaneously or subsequently, accessory cells can be additionally bound via the Fc region of the Triomab® antibody. A process of mutual cross-talk between T-cells and accessory immune cells (macrophages, DCs and NK cells) is initiated via costimulatory molecules and cytokines.
[Source: Ruf & Lindhofer, Blood 98, 2526-34, 2001]
T-cells are strongly activated in a physiological manner (1), receiving a second co-stimulatory signal (signal 2), while accessory immune cells are stimulated via Fcγ-RI/IIa or III crosslinking.
As a result, tumor cells are effectively destroyed by a concerted attack of T-cells and accessory immune cells applying different killer mechanisms like perforin/granzyme-mediated lysis and apoptosis induction (2), or antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and phagocytosis (3).
Finally, T cell proliferation occurs as well as necrotic or apoptotic tumor particles are phagocytosed, processed, and presented by stimulated professional antigen-presenting cells (macrophages, DCs). This can lead to the induction of a patient-specific and long-term anti-tumor immunization effect (4).
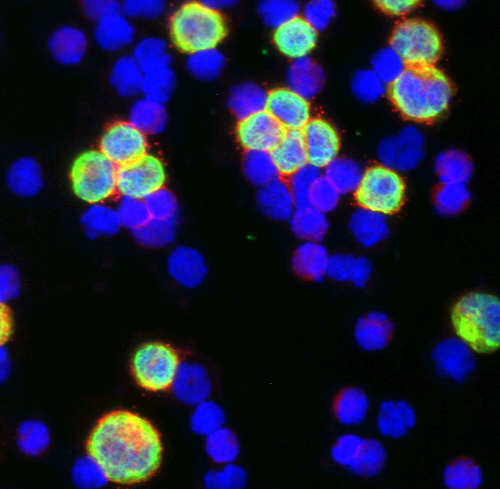
Immunofluorescence staining of Triomab® antibody-induced immune cell complexes
Triomab® antibodies induce multiple immune cell complexes
As shown by the example (picture on the left side – desktop / above- mobile) Triomab® antibodies initiate the formation of multiple complexes between tumor cells and human immune effector cells:
EpCAM positive human tumor cells (HCT-8, stained in green by anti-cytokeratin 8, 18, and 19 FITC) are surrounded by and connected to human immune effector cells (PBMC, cell nucleus staining in blue) via EpCAM x CD3 bispecific Triomab® antibodies in red (texas red) functioning like a zipper between different cell types.
Advantages of Triomab® antibodies used in oncology
Effective at low therapeutic dosages in the microgram (µg) range
Full physiological activation of the patients’ most important cancer-fighting immune cells at the tumor site
Linking innate and adaptive immunity resulting in vaccination-like effects against individual mutations of the patient’s cancer
Image Credits: NDABCREATIVITY | 189627906 | Adobe Stock / Graphics: Lindis Biotech GmbH